What is Eczema?
Eczema is the name given to a group of diseases that cause inflammation of the skin. It is also often called Dermatitis. Eczema on hands and elsewhere in the body is a chronic problem for many people in the United States, with an estimated 35 million Americans experiencing it. Seventy percent of those cases start in children younger than 5 years of age. When an eczema flare-up occurs, the skin will become red, itchy, and swollen with fluid-filled bumps that sometimes ooze and crust. Eczema is often caused by an allergic reaction, and it is not contagious. It can also be hereditary, but it is not curable. Flare-ups are, however, successfully managed with treatment [1]. There are several different types of eczema, and they all affect the body differently, one of the most common being dyshidrotic eczema.
Read: What Are Those Little White Bumps on Your Skin, and What to Do About Them
What is Dyshidrotic Eczema?
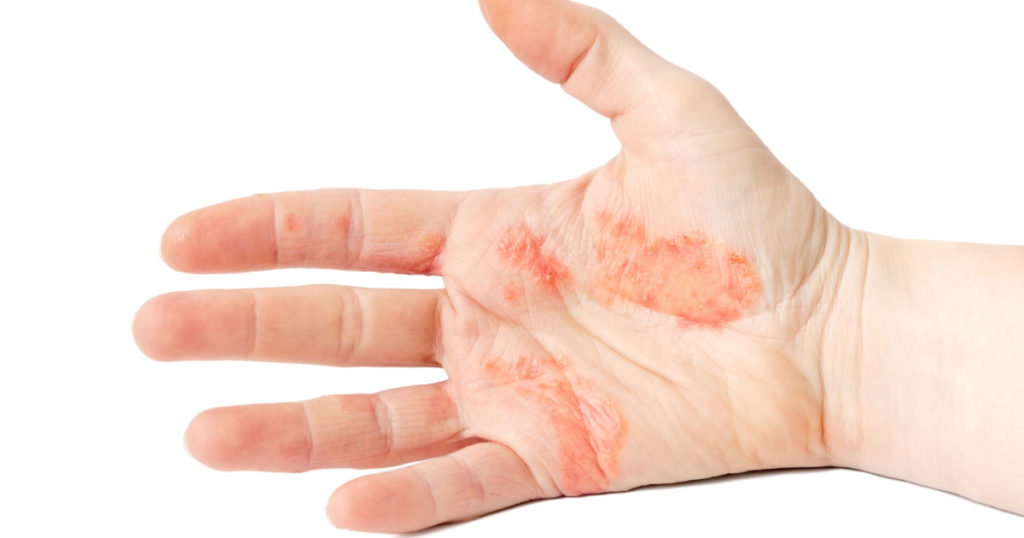

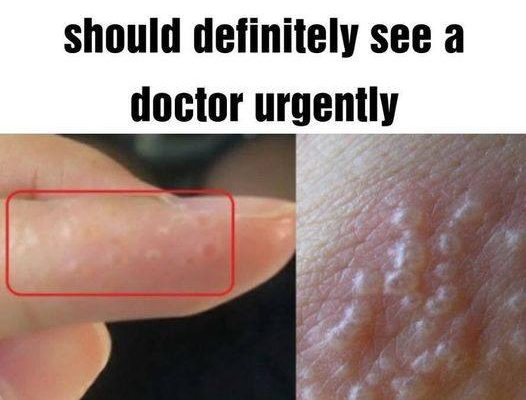
Dyshidrotic eczema is a common type of eczema that causes small, intensely itchy blisters to form on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles of the feet. Dyshidrotic eczema is associated with seasonal allergies, and, because of this, the blisters are more likely to erupt in the spring. These blisters can be very painful, and can sometimes take weeks to disappear [2].
If you haven’t heard of this type of eczema before, don’t fret, it does have a few other names that it goes by, including [3]:
- Pedopompholyx (affects the feet)
- Cheiropompholyx (affects the hands)
- Vesicular palmoplantar eczema
- Dyshidrosis
- Foot-and-hand eczema
- Dyshidrotic dermatitis
- Vesicular eczema
- Pompholyx
Symptoms of Dyshidrotic Eczema
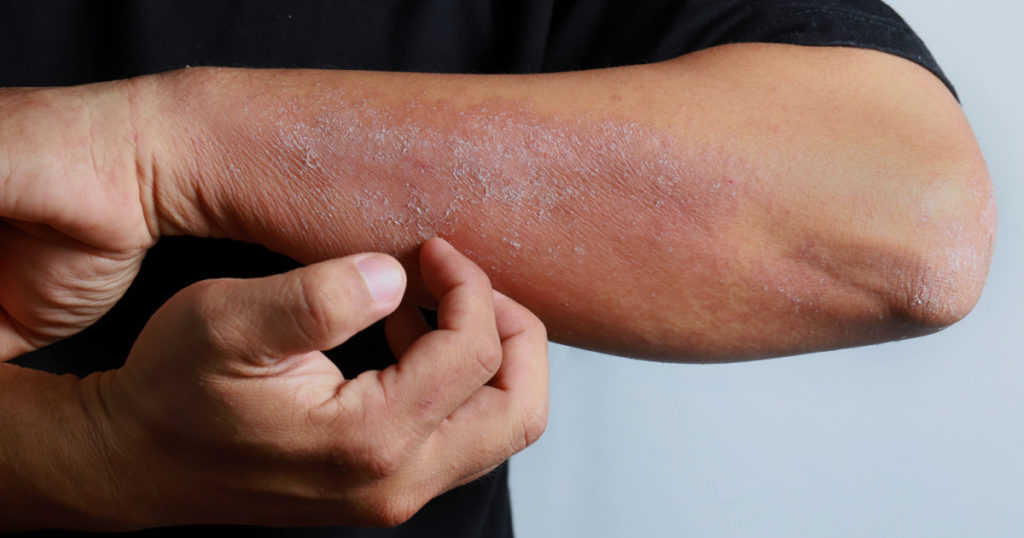
Each type of eczema varies slightly in the way that it presents itself, and so the treatment also varies slightly. So, in order to know how to treat yourself, it’s important to recognize your dyshidrotic eczema for what it is. All forms of eczema cause inflammation to the skin, yet they are each different in their own ways. Correctly identifying your dyshidrotic eczema is the first step in relieving your symptoms.
Common dyshidrotic eczema symptoms include [3]:
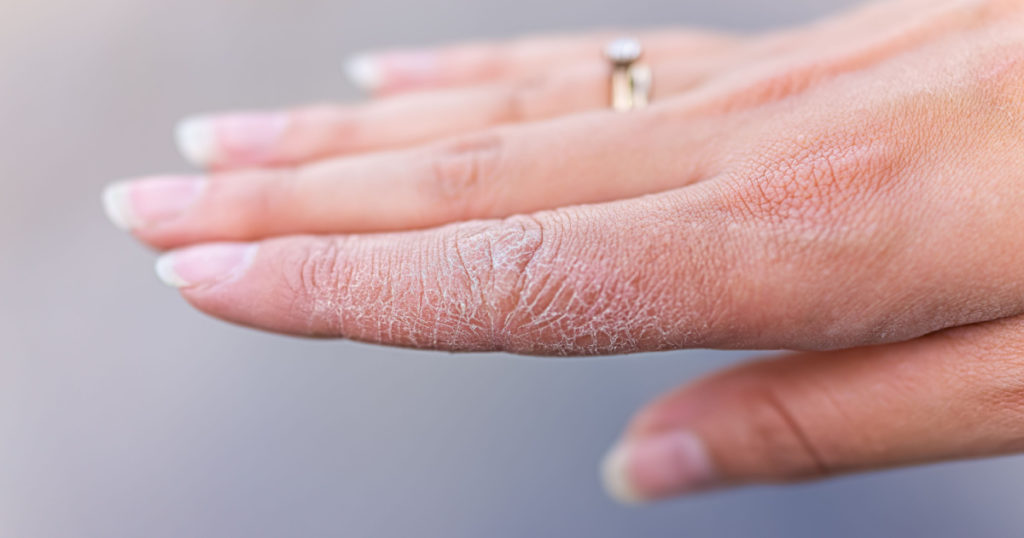

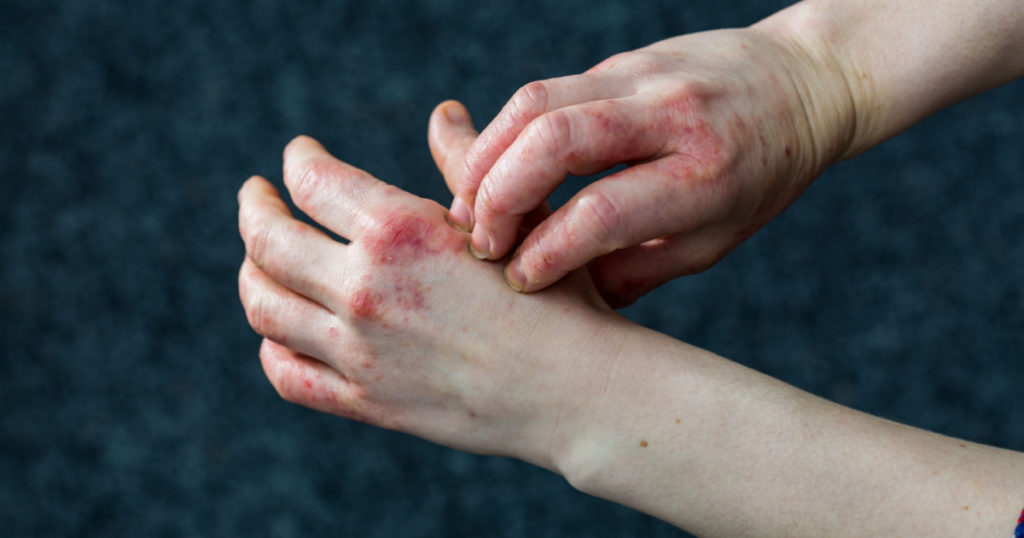
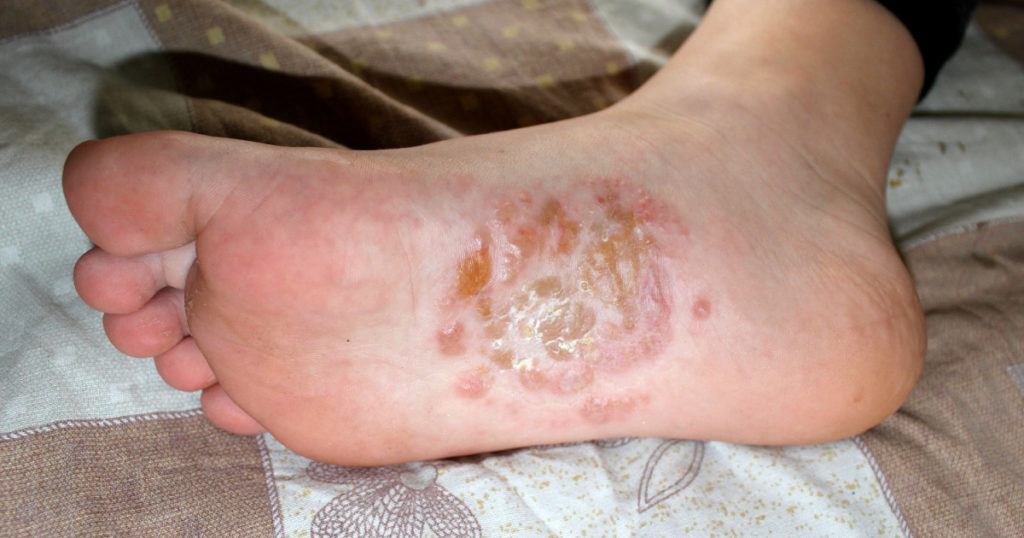
- Deep-set blisters on hands and feet (specifically on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles of the feet)
- Itching
- Redness
- Flaking
- Scaly, cracked skin
- Pain
What Causes Dyshidrotic Eczema?
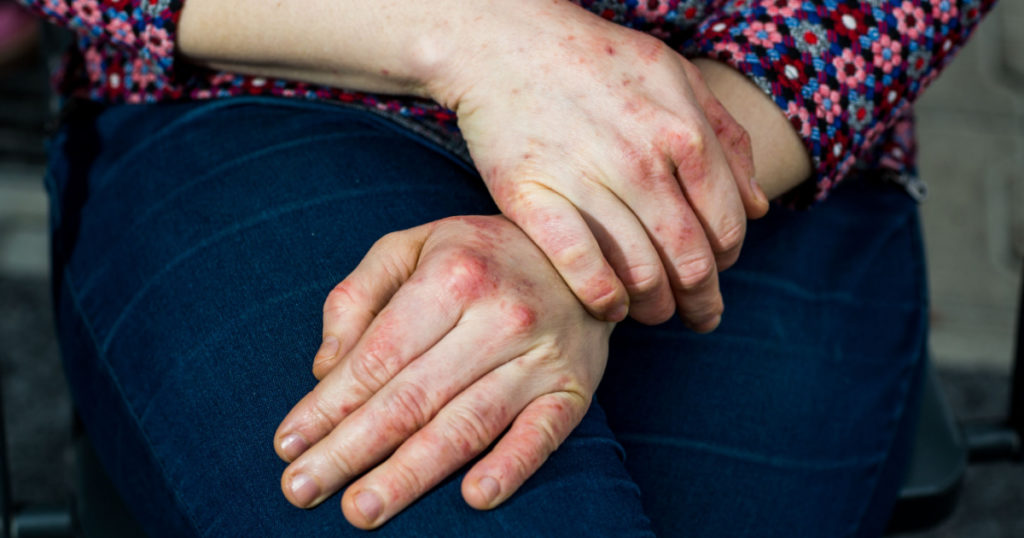

Dyshidrotic eczema is twice as common in women as it is in men, and while it can occur in people of any age, it is most common in adults aged 20-40. People with contact dermatitis, atopic eczema, or hay fever are at a higher risk of developing dyshidrotic eczema. It also is hereditary, so if you have a close relative that has dyshidrotic eczema than your likelihood of getting it increases [3]. Dyshidrotic eczema does have a tendency to get infected, which delays the healing process [3]. If you believe that this is the case for you, then contact your healthcare provider immediately to seek advanced treatment.
Read: Family is sharing their story of tragic loss to raise awareness about allergies
How to Treat Dyshidrotic Eczema on Hands
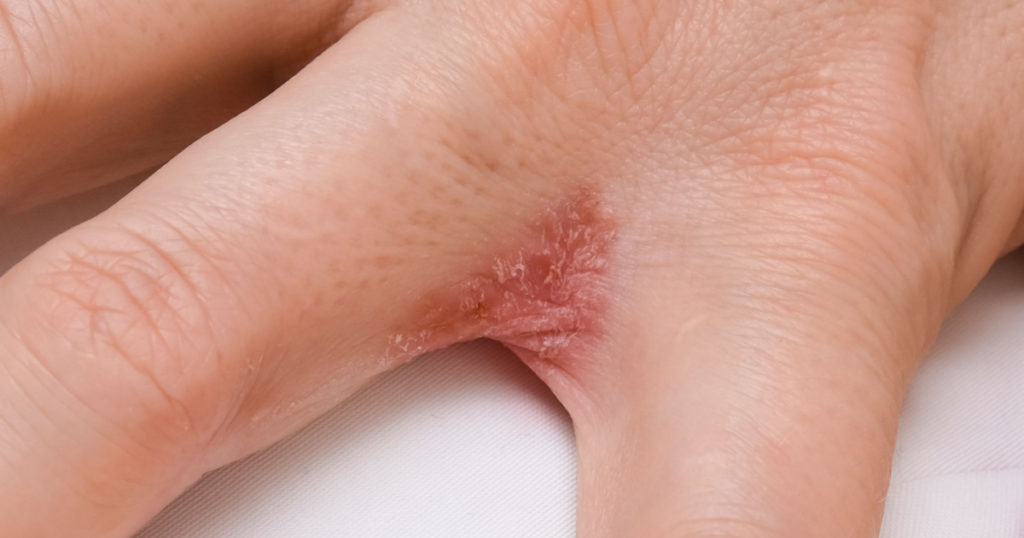
Unfortunately, dyshidrotic eczema is not curable, but in many cases, it is manageable with treatment. While there is no surefire way to prevent flare-ups from happening, a good skincare regime can help to strengthen your skin against inflammation.
Conventional Treatment
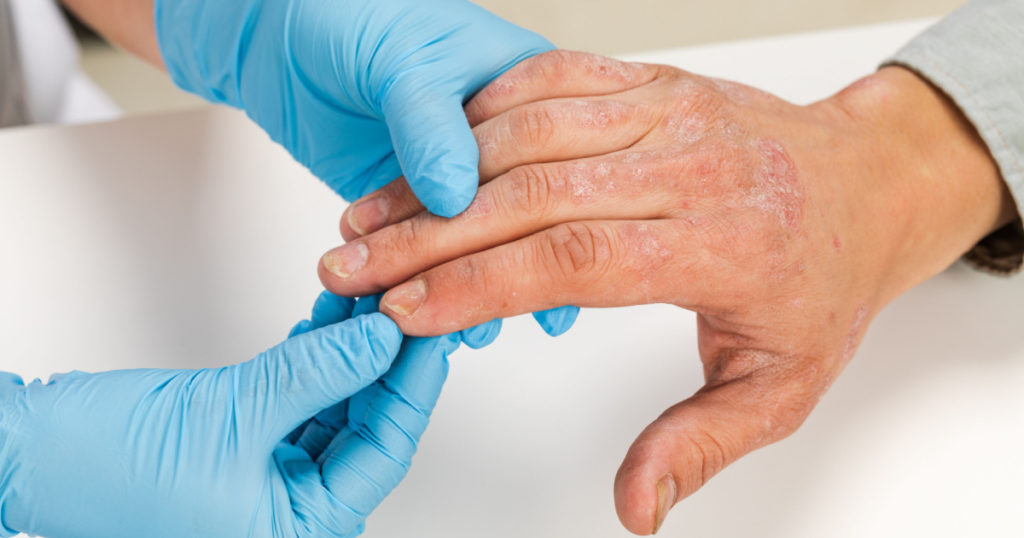
While most cases of dyshidrotic eczema may be handled with natural treatments that are less invasive to the body, severe cases are often remedied with dyshidrotic eczema treatment cream (e.g., a corticosteroid cream or ointment or a prescribed injection or pill).
Some other treatments include [4]:
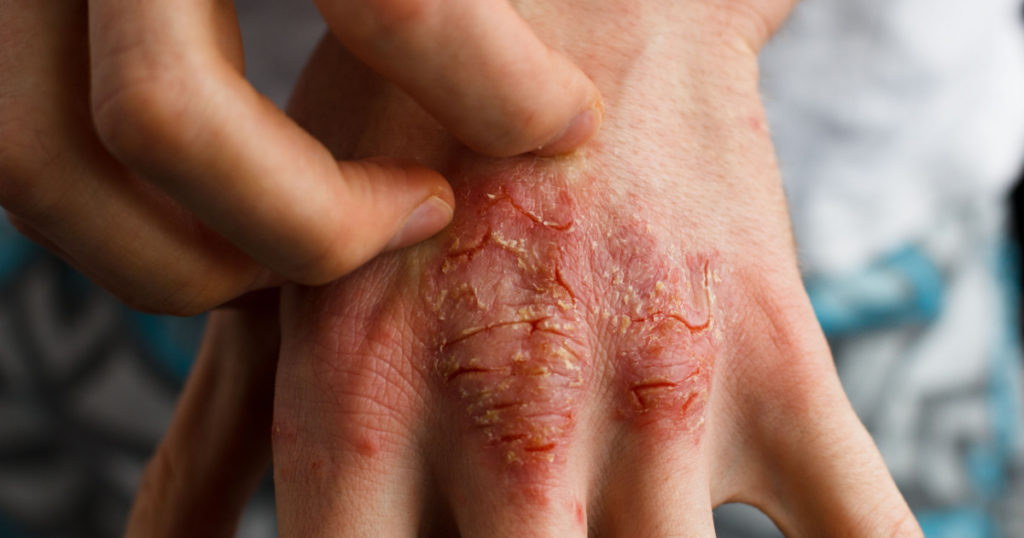
- UV light treatments
- draining large blisters
- antihistamines
- various anti-itch creams
- immune-suppressing ointments, such as Protopic and Elidel